
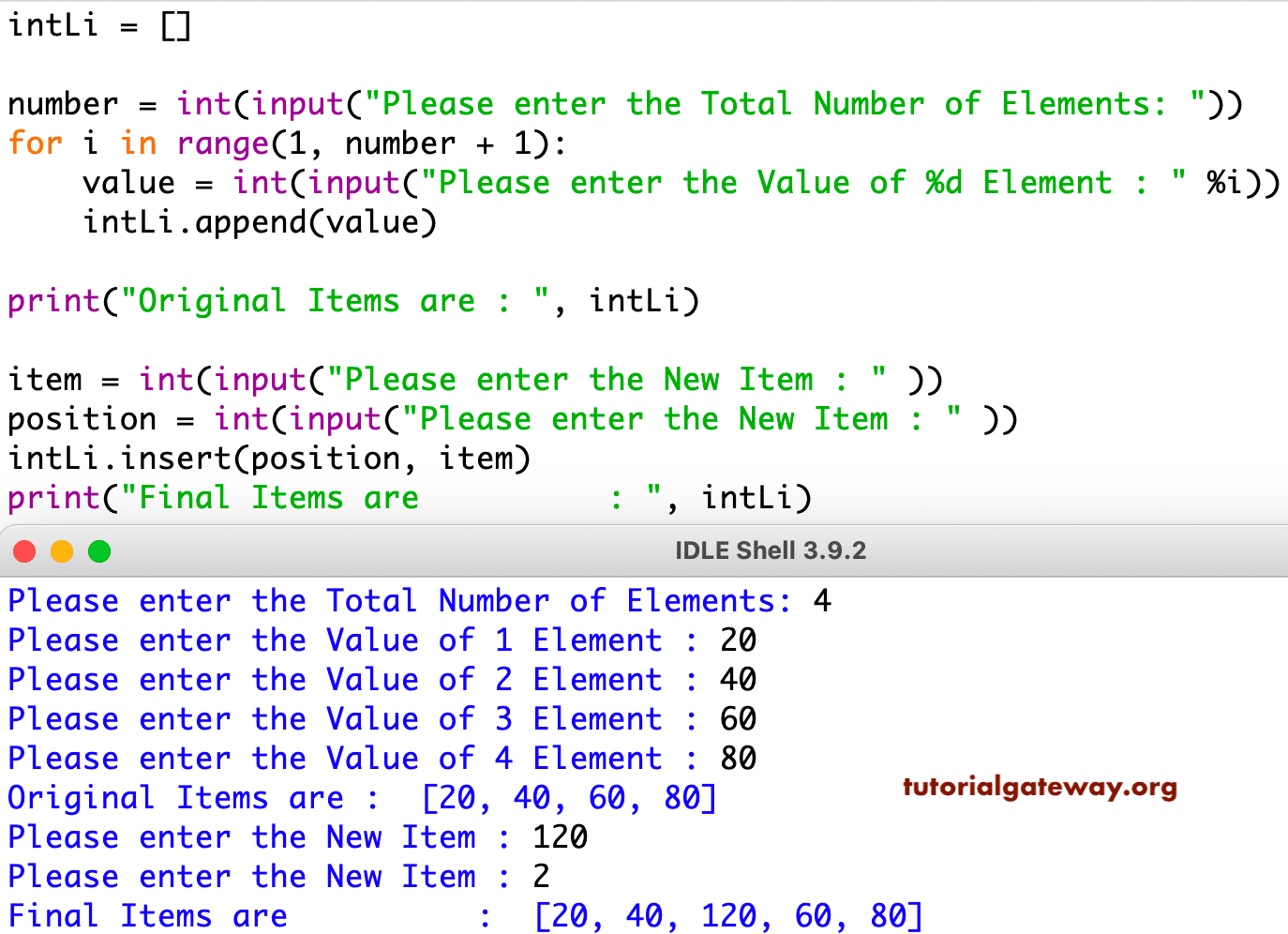
append() works in other data structures, such as array.array() and que(). In the next two sections, you’ll learn how. However, there are some subtle differences. The method adds a single item to the end of the underlying data structure. The operating principle is the same as the traditional. Other Python data structures also implement. You can use Queue the same way you used Stack in the above section: just call. The rest of the implementation is almost identical but uses appropriate names, such as. You’ll learn more about using deques a little later in the tutorial. popleft() as an efficient way of consuming items from the beginning of the deque(). Luckily, Python’s collections module provides a data structure called deque(), which implements. pop(0) on a Python list isn’t the most efficient way of consuming list items. It returns the item at that index in the underlying list and also removes the item: pop(), which optionally takes an integer index as an argument. append() is equivalent to a push operation, so you can use it to push items onto the stack. pop removes and returns the item at the top of the stack.

Implementing a StackĪ stack is a data structure that stores items on top of each other.
#Python add to list how to#
In this section, you’ll learn how to use a Python list to create stack and queue data structures with the minimal required functionality using. Now it’s time for a different and more specific kind of example. append() to add a single item to a list or to populate lists from scratch. Creating Stacks and Queues With Python’s. append() with a list comprehension or with any other construct. The moral behind the above example is that there are some situations in which you can’t replace.
#Python add to list code#
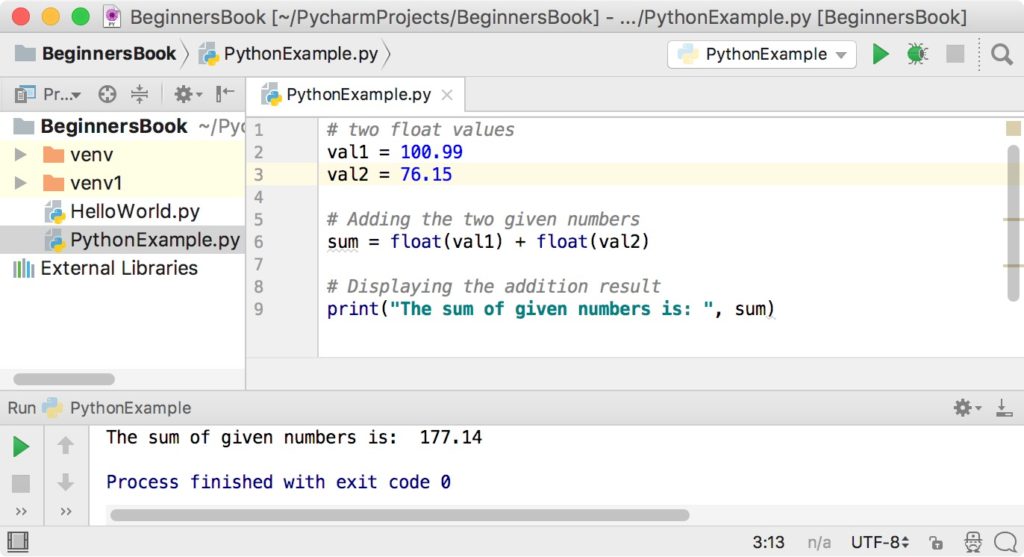
Using print() inside a list comprehension doesn’t seem coherent or even possible unless you wrap part of the code in a helper function. Now think of how you can turn the body of square_root() into a list comprehension. > numbers = > square_root ( numbers ) Processing number: 1 Completed: 11%. > import math > def square_root ( numbers ). Say you need to create a function that takes a sequence of numbers and returns a list containing the square root of each number: append() to add successive results to the list. Inside the loop, you can manipulate the data and use. append() is to completely populate an empty list using a for loop. In the next few sections, you’ll learn how and when to use these techniques to create and populate Python lists from scratch. Populating a List From ScratchĪ common problem that you might face when working with lists in Python is how to populate them with several items for further processing. append() in mind will help you prevent errors in your code. append() is a common mistake when it comes to learning how mutable sequence types work. append() changes the underlying list in place.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
